|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The Ozone Hole 2024
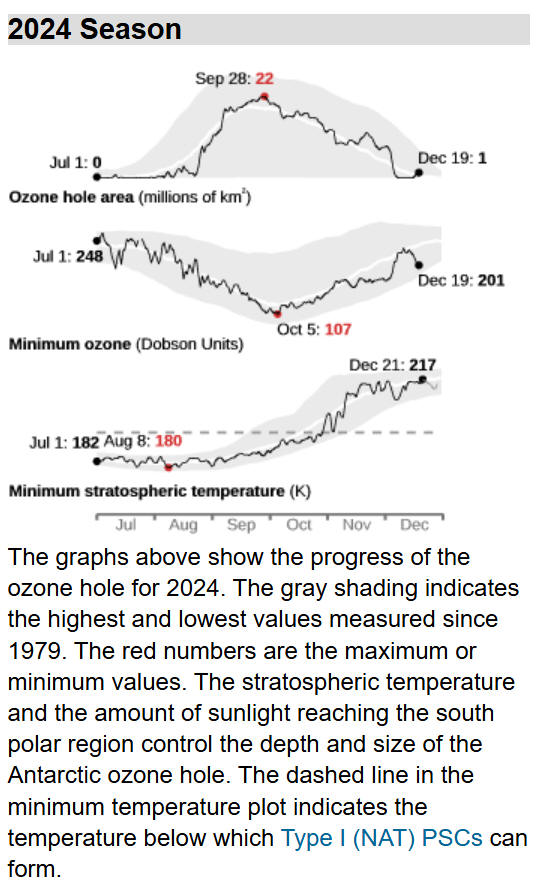
Antarctic Situation at 2024 December 16
Antarctic ozone
today:
The 2024
ozone hole is over.
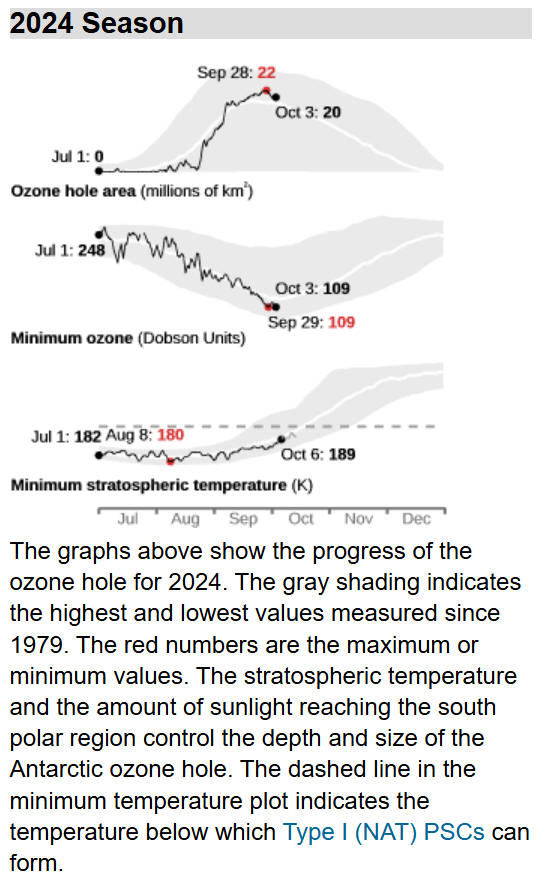
It began
to appear in late August and grew rapidly to reach a peak of 22
million
square kilometres (msqkm) in late September, a little larger than
the average over the last decade, but smaller than the previous two
years. It shrank during the first ten days of October, but then
remained at around 16 msqkm until late in the month. It had shrunk
to 9 msqkm by early November and remained near that size for most of
the month. It shrank rapidly in early December and was gone by the
7th, a little earlier than the mean for the last decade. The 2024
polar vortex began to form in late April, a little earlier than
usual. It grew steadily and reached a maximum of around 31 msqkm in
early September. It slowly shrank, the decline becoming more rapid
in December and it currently has an area of around 12 msqkm, above
the usual area. Within the vortex the ozone layer temperature is now
above the -78°C Polar Stratospheric Clouds (PSC) formation threshold
throughout the ozone layer and is rising. The temperature of the
ozone layer is now warmest over Antarctica and declines towards the
equator. The area with potential PSCs began to grow from mid May and
reached 24 msqkm in late July.
Some
warming events then took place around the time when the area is
usually at its peak, reducing it to 20 msqkm. It grew again to reach
23 msqkm in mid August, but had disappeared by the end of October.
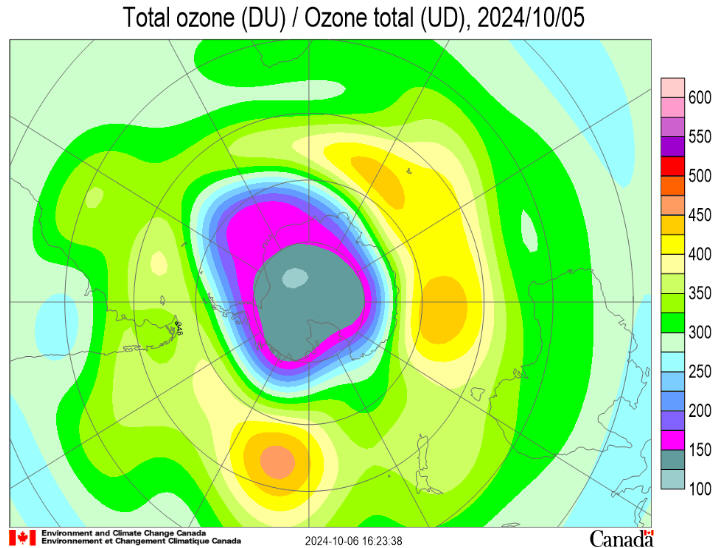
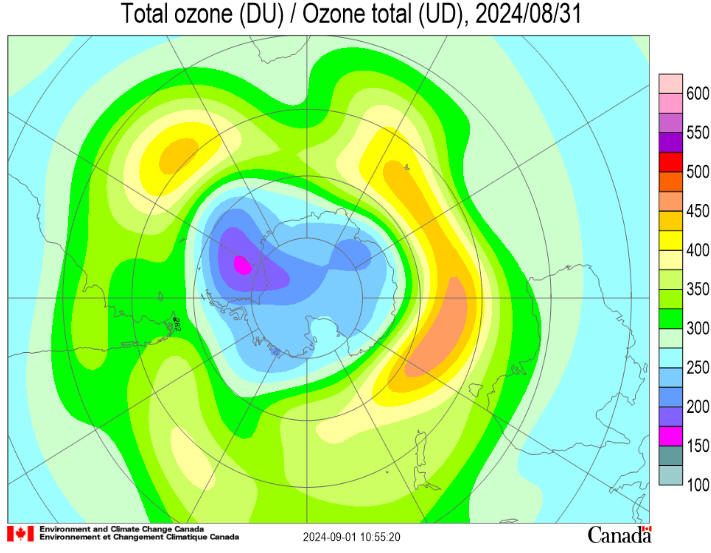
Ozone values remain much lower over the continent and higher over
the southern ocean. They currently range from a low of around 240
Dobson Units (DU) to a high of around 380 DU. The lowest ozone value
reported by NASA was 107 DU on October 5. The ozone hole became more
elongated over the first few days of October and the edge clipped
the tip of South America, the Falkland Islands and South Georgia. It
did so again between October 11 and 13.
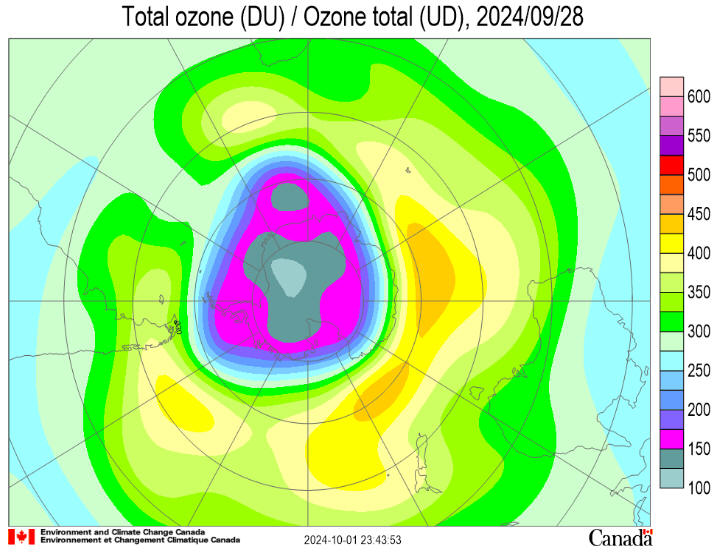
October 30, 2024 NASA, NOAA Rank 2024 Ozone Hole as 7th-Smallest Since Recovery Began Healing continues in the atmosphere over the Antarctic: a hole that opens annually in the ozone layer over Earth’s southern pole was relatively small in 2024 compared to other years. Scientists with NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) project the ozone layer could fully recover by 2066. During the peak of ozone depletion season from Sept. 7 through Oct. 13, the 2024 area of the ozone hole ranked the seventh smallest since recovery began in 1992, when the Montreal Protocol, a landmark international agreement to phase out ozone-depleting chemicals, began to take effect. At almost 8 million square miles (20 million square kilometers), the monthly average ozone-depleted region in the Antarctic this year was nearly three times the size of the contiguous U.S. The hole reached its greatest one-day extent for the year on Sept. 28 at 8.5 million square miles (22.4 million square kilometers).
The improvement is due to a combination of continuing declines in harmful chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) chemicals, along with an unexpected infusion of ozone carried by air currents from north of the Antarctic, scientists said. In previous years, NASA and NOAA have reported the ozone hole ranking using a time frame dating back to 1979, when scientists began tracking Antarctic ozone levels with satellite data. Using that longer record, this year’s hole ranked 20th smallest in area across the 45 years of observations. “The 2024 Antarctic hole is smaller than ozone holes seen in the early 2000s,” said Paul Newman, leader of NASA’s ozone research team and chief scientist for Earth sciences at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. “The gradual improvement we’ve seen in the past two decades shows that international efforts that curbed ozone-destroying chemicals are working.” The ozone-rich layer high in the atmosphere acts as a planetary sunscreen that helps shield us from harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the Sun. Areas with depleted ozone allow more UV radiation, resulting in increased cases of skin cancer and cataracts. Excessive exposure to UV light can also reduce agricultural yields as well as damage aquatic plants and animals in vital ecosystems. Scientists were alarmed in the 1970s at the prospect that CFCs could eat away at atmospheric ozone. By the mid-1980s, the ozone layer had been depleted so much that a broad swath of the Antarctic stratosphere was essentially devoid of ozone by early October each year. Sources of damaging CFCs included coolants in refrigerators and air conditioners, as well as aerosols in hairspray, antiperspirant, and spray paint. Harmful chemicals were also released in the manufacture of insulating foams and as components of industrial fire suppression systems. The Montreal Protocol was signed in 1987 to phase out CFC-based products and processes. Countries worldwide agreed to replace the chemicals with more environmentally friendly alternatives by 2010. The release of CFC compounds has dramatically decreased following the Montreal Protocol. But CFCs already in the air will take many decades to break down. As existing CFC levels gradually decline, ozone in the upper atmosphere will rebound globally, and ozone holes will shrink. “For 2024, we can see that the ozone hole’s severity is below average compared to other years in the past three decades, but the ozone layer is still far from being fully healed,” said Stephen Montzka, senior scientist of the NOAA Global Monitoring Laboratory. Researchers rely on a combination of systems to monitor the ozone layer. They include instruments on NASA’s Aura satellite, the NOAA-20 and NOAA-21 satellites, and the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership satellite, jointly operated by NASA and NOAA. NOAA scientists also release instrumented weather balloons from the South Pole Baseline Atmospheric Observatory to observe ozone concentrations directly overhead in a measurement called Dobson Units. The 2024 concentration reached its lowest value of 109 Dobson Units on October 5. The lowest value ever recorded over the South Pole was 92 Dobson Units in October 2006. NASA and NOAA satellite observations of ozone concentrations cover the entire ozone hole, which can produce a slightly smaller value for the lowest Dobson Unit measurement. “That is well below the 225 Dobson Units that was typical of the ozone cover above the Antarctic in 1979,” said NOAA research chemist Bryan Johnson. “So, there’s still a long way to go before atmospheric ozone is back to the levels before the advent of widespread CFC pollution.” View the latest status of the ozone layer over the Antarctic with NASA’s ozone watch.
By James
Riordon
Media Contact:
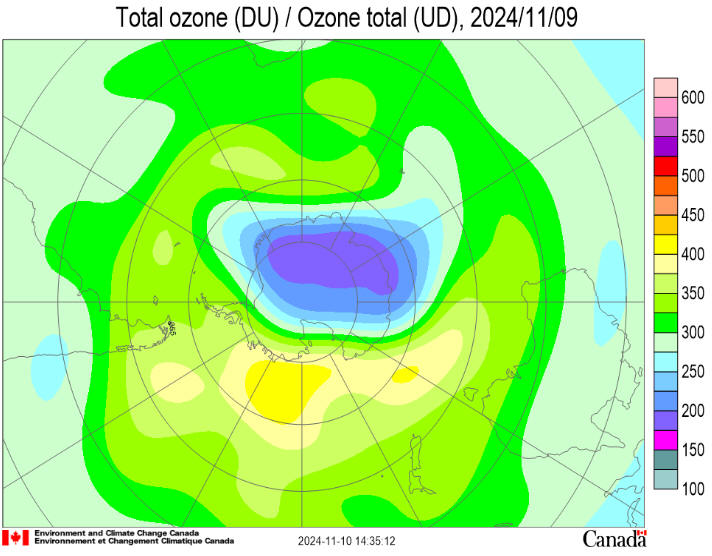
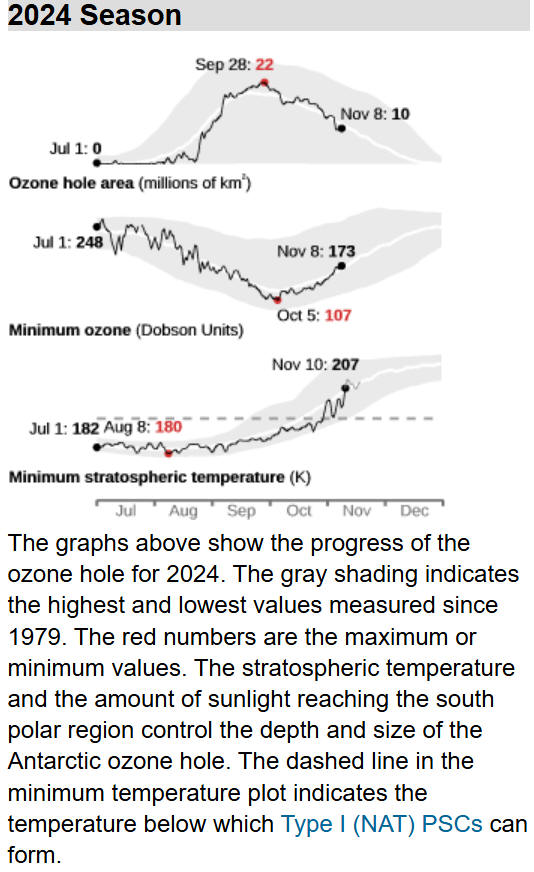
Antarctic Situation at
2024 November 4
Antarctic ozone today:
The 2024 ozone hole began to appear in late August and grew rapidly
to reach a peak of 22
million square kilometres (msqkm) in late September, a little larger
than the average over the last decade, but smaller than the previous
two years. It shrank during the first ten days of October, but then
remained at around 16 msqkm until late in the month. It has now
shrunk to 11 msqkm. The 2024 polar vortex began to form in late
April, a little earlier than usual. It grew steadily and reached a
maximum of around 31 msqkm in early September. It currently has an
area of around 25 msqkm, close to the usual area. Within the vortex
the ozone layer temperature is now above the -78°C Polar
Stratospheric Clouds (PSC) formation threshold throughout the ozone
layer and is rising. The temperature of the ozone layer is warmest
over the Southern Ocean and declines towards the equator and the
remaining centre of the vortex. The area with potential PSCs began
to grow from mid May and reached 24 msqkm in late July.
Some warming events then took place around the time when the
area is usually at its peak, reducing it to 20 msqkm. It grew again
to reach 23 msqkm in mid August, but had disappeared by the end of
October. Ozone values are much lower over the continent and higher
over the southern ocean. They currently range from a low of around
160 Dobson Units (DU) to a high of around 410 DU. The lowest ozone
value reported by NASA is 107 DU on October 5. The ozone hole became
more elongated over the first few days of October and the edge
clipped the tip of South America, the Falkland Islands and South
Georgia. It did so again between October 11 and 13. The ozone
hole/vortex has again become very elongated, but is expected to
return to more circular symmetry over the coming ten days.
NASA Ozone Watch: Latest status of ozone
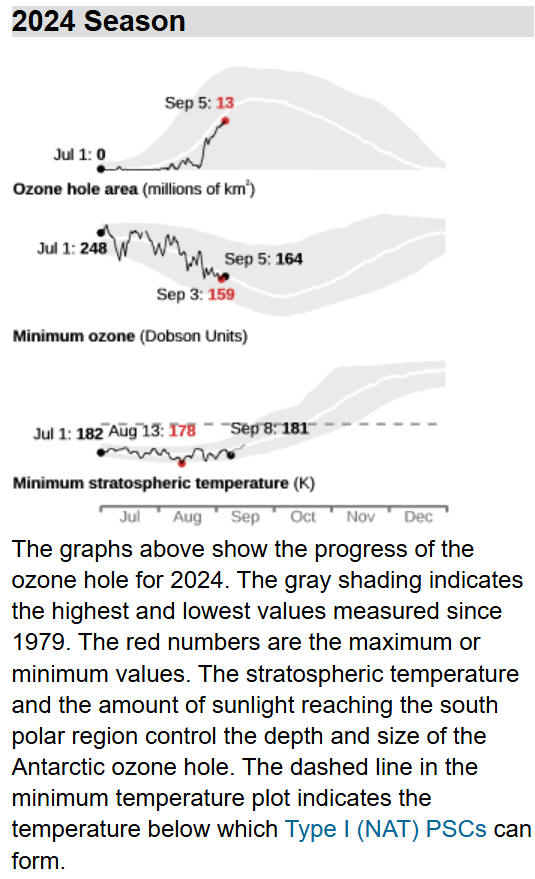
Antarctic Situation at 2024 September 30
Antarctic ozone
today:
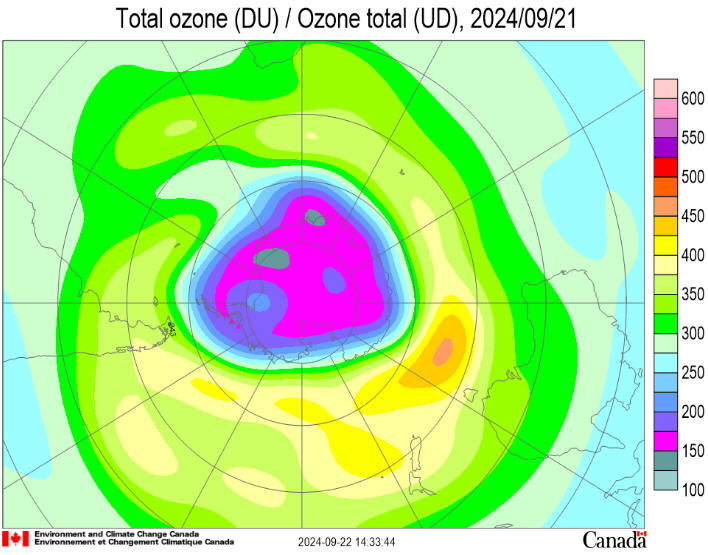
The 2024
ozone hole began to appear in late August and has grown rapidly. It
now covers 21
million
square kilometres (msqkm), close to the average over the last
decade. It is near its maximum size and depth for the year. The 2024
polar vortex began to form in late April, a little earlier than
usual. It grew steadily and reached a maximum of around 31 msqkm in
early September. It currently has an area of around 30 msqkm, a
little smaller than the usual area. Within the vortex the ozone
layer temperature is well below the -78°C Polar Stratospheric Clouds
(PSC) formation threshold. The temperature has passed the annual
minimum, and is rising at the top of the ozone layer. The
temperature of the ozone layer is warmest over the Southern Ocean
and declines towards the equator and pole. The area with potential
PSCs began to grow from mid May and reached 24 msqkm in late July.
Some
warming events then took place around the time when the area is
usually at its peak, reducing it to 20 msqkm. It grew again to reach
23 msqkm in mid August, but is now declining and has reached 15
msqkm, a little larger than usual for the time of year. Overall the
system has now become more stable. Ozone values are much lower over
the continent and higher over the southern ocean. They currently
range from a low of around 120 Dobson Units (DU) to a high of around
430 DU. The ozone hole is expected to become more elongated over the
next few days and the edge will clip the tip of South America, the
Falkland Islands and South Georgia over the first few days of
October.
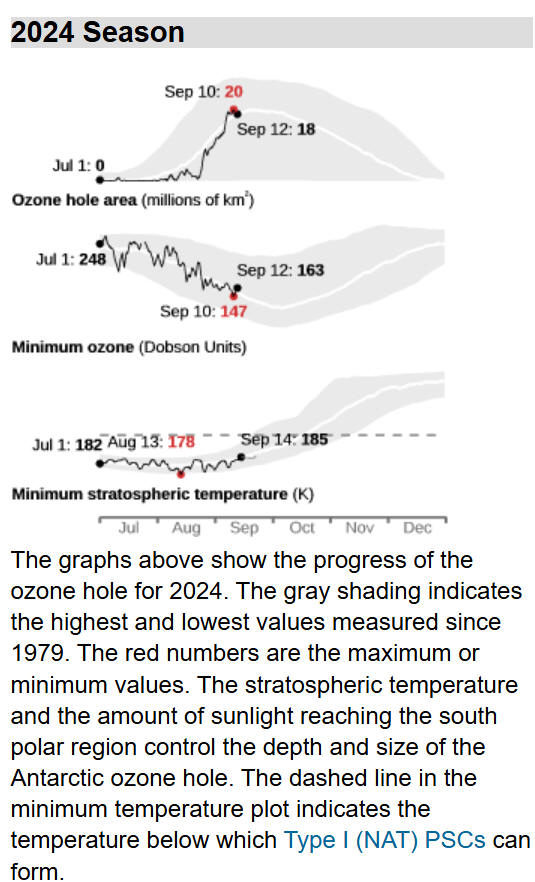
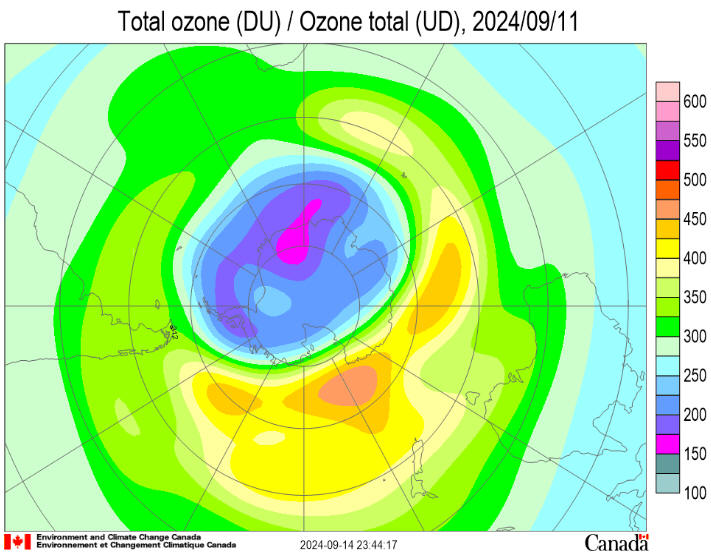
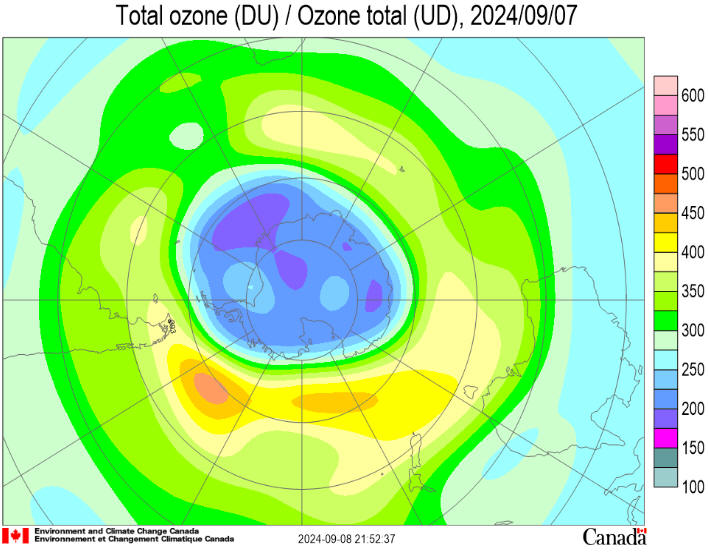
Antarctic Situation at
2024 September 16
Antarctic ozone
today:
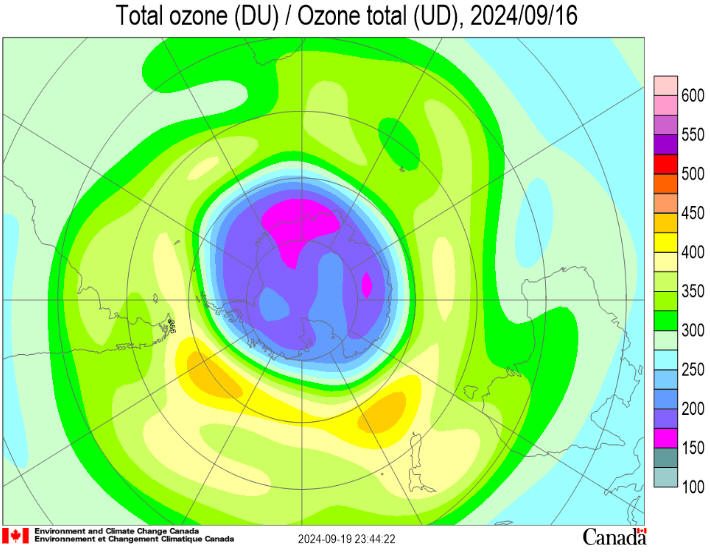
The 2024
ozone hole began to appear in late August and has grown rapidly. It
now covers 16
million
square kilometres (msqkm). The temperature of the ozone layer over
Antarctica is near the annual minimum, with air descending over the
south pole. The temperature of the ozone layer is warmest over the
Southern Ocean and declines towards the equator and pole. The 2024
polar vortex began to form in late April, a little earlier than
usual. It has grown and currently has an area of around 31 msqkm, a
little smaller than the usual area. Within the vortex the
temperature is now well below the -78°C Polar Stratospheric Clouds
(PSC) formation threshold. The area with potential PSCs began to
grow from mid May and reached 24 msqkm in late July.
Some
warming events then took place around the time when the area is
usually at its peak, reducing it to 20 msqkm. It grew again to reach
23 msqkm in mid August, but is now declining and has reached 17
msqkm, close to usual for the time of year. Overall the system has
now become more stable. Ozone values are much lower over the
continent and higher over the southern ocean. They currently range
from a low of around 160 Dobson Units (DU) to a high of around 430
DU. The ozone hole is expected to grow in area and depth over the
coming week.
NASA Ozone Watch: Latest status of ozone
Antarctic Situation at 2024
NASA Ozone Watch: Latest status of ozone
Antarctic Situation at 2024 August 28
Antarctic Situation at 2024 August 5
Antarctic Situation at 2024 July 22 Antarctic ozone today: The temperature of the ozone layer over Antarctica is nearing the annual minimum, with air descending over the south pole. The temperature of the ozone layer is warmest over the Southern Ocean and declines towards the equator and pole. The 2024 polar vortex began to form in late April, a little earlier than usual. It has grown and currently has an area of around 25 million square kilometres (msqkm), close to the usual area. Within the vortex the temperature is now well below the -78°C Polar Stratospheric Clouds (PSC) formation threshold. The area with potential PSCs began to grow from mid May and is currently around 23 msqkm, a little lower than usual for the time of year. Overall the system is relatively unstable, with significant wave activity. Ozone values are a little lower over the continent and higher over the southern ocean. They currently range from a low of around 240 Dobson Units (DU) to a high of around 480 DU.
Antarctic Situation at 2024 July 8Antarctic ozone today:
The temperature of the ozone layer over Antarctica is falling
and air is descending over the south pole. The temperature of the
ozone layer is warmest over the Southern Ocean and declines towards
the equator and pole. The 2024 polar vortex began to form in late
April, a little earlier than usual. It has grown and currently has
an area of around 22 million square kilometres (msqkm), close to the
usual area. Within the vortex the temperature is now below the -78°C
Polar Stratospheric Clouds (PSC) formation threshold. The area with
potential PSCs began to grow from mid May and is currently around 22
msqkm. Overall the system is relatively unstable, with significant
wave activity. Ozone values are a little lower over the continent
and higher over the southern ocean. They currently range from a low
of around 260 Dobson Units (DU) to a high of around 430 DU.
Antarctic Situation at
2024 June 24
|